Manufacturing Execution System (MES)
The Complete Guide
Learn about what an MES is, how it works, how it can benefit operations, and empower businesses to succeed. This complete guide aims to provide you with an in-depth comprehension of the multiple facets of Smart Manufacturing overseen by a Manufacturing Execution System (MES).
What is an MES?
A Manufacturing Execution System, or MES, is a Manufacturing Operations Management (MoM) system. This is a type of digital solution that aims to provide an executive control of all the facets of an operational floor (Such as Production, Quality, Maintenance, etc.) By interconnecting and keeping track of all your assets (equipment, digital hardware) in a digital ecosystem, you can proactively adjust processes, prevent mishaps, and empower your teams to do what they do best.
Table of content
What does an MES do?
Oftentimes, manufacturers realize that what they relied on from the start is just not enough to sustain their ambitions. Many of the systems that were sought out to manage the executive aspects eventually fall short of providing the right support for executives and operators.
From the inception of the MESA Model to the more recent Strategic Initiatives, Smart Manufacturing encapsulates a wide range of solutions to cater to the increasing demand of digital solutions. Depending on the level of automation, manufacturers can look into the synergy of smart manufacturing and find a solution that suits their needs. Essentially, an integrated MES can empower operators and increase overall efficiency.
Core MES functionalities
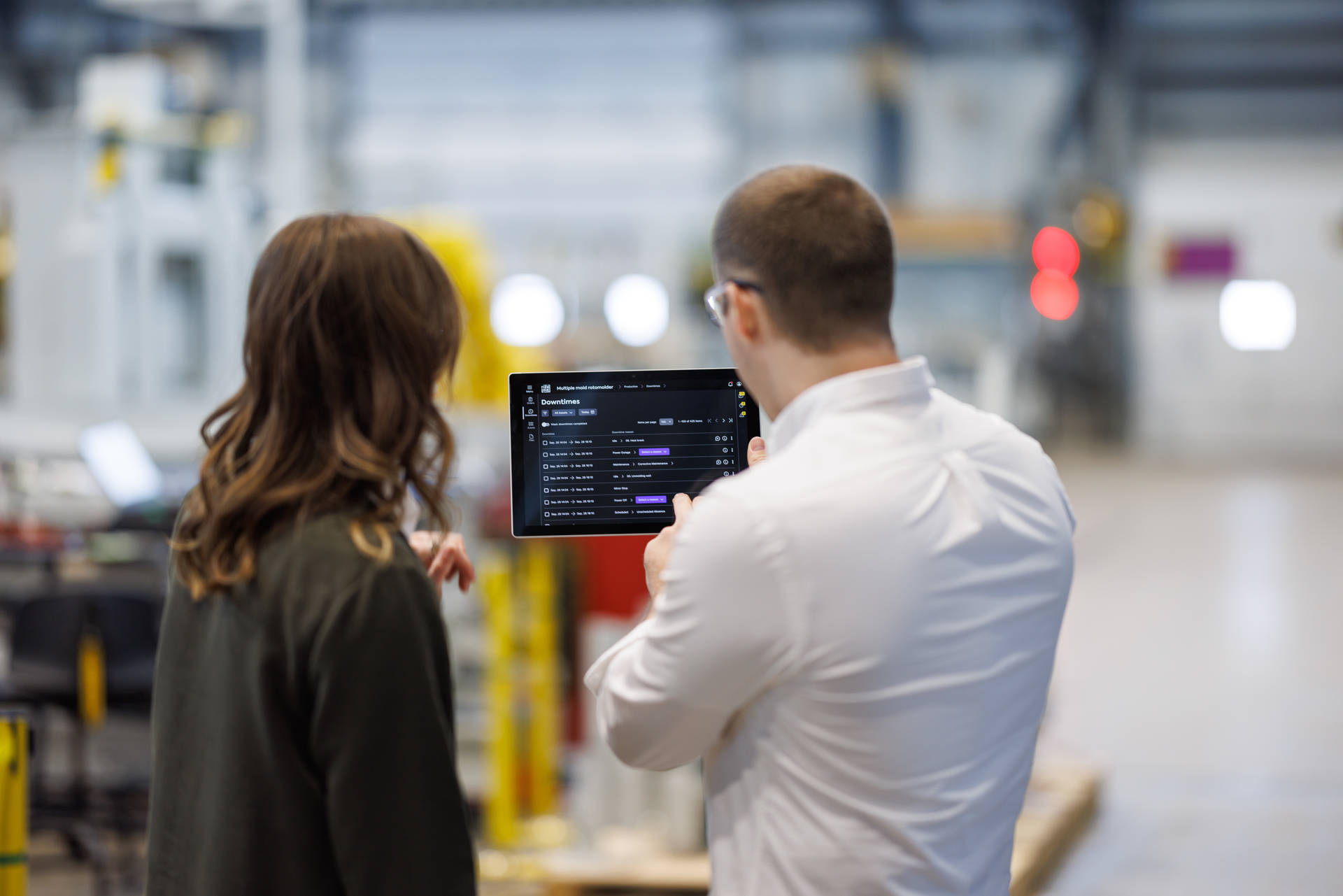
The MES distinguishes itself by offering a comprehensive overview of manufacturing and by highlighting the focal points of manufacturing. These points can range from production management and workorder completion, to full-depth quality tracking and genealogy. As such, an integrated MES effectively grants you a bird’s-eye view of your manufacturing floor, as well as a transparent communication of data between operators.
A MES will typically have a set of core functionalities that overview planning, through resources, orders, and employee administration. The MES will also support all areas of management through information access, organization, and maintenance. The performance analysis and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE ) visualizations allow synthesizing production in terms of machine process and quality. Finally, this interconnectivity allows for a greater flexibility in terms of quality management, and real-time production monitoring.

Data collection and acquisition
Data collection is truly a key focus when it comes to smart manufacturing and industry 4.0.
Data collection is made possible by connecting equipment to track and gather data throughout manufacturing processes in real time. By organizing and centralizing data, you're empowered to have a complete and transparent overview of your operation. This investment enabler lets you see the operation in a new light and empowers your teams to optimize key processes to maximize productivity based on the gathered data.

Performance analysis
Performance analysis is the core of MES utilization. Although performance tracking and analysis seems to be a tedious task that usually requires a lot of time, knowledge, and dedication to manage, an MES makes it a breeze.
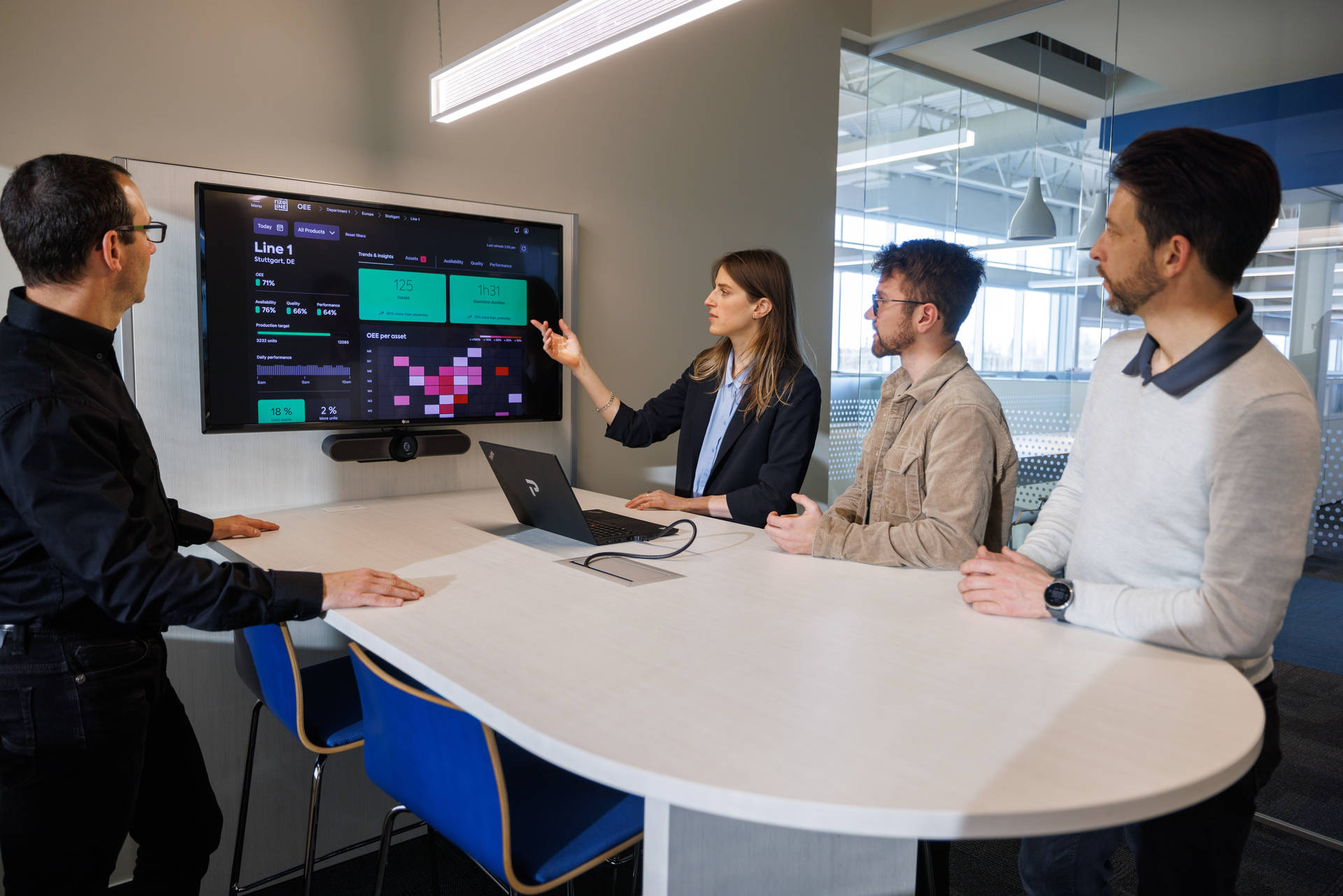
MES interconnectivity and data tracking encode important information like production cycle time, resource utilization, and downtime, among other things. These allow your entire operation to work with the same real-time information. Data is consolidated on a range of user-friendly dashboards. This lets you oversee operational constraints, find the best ways to tackle them, and calculate your Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE).
The OEE synthesizes and identifies what is affecting production. It helps find solutions quicker by correlating product quality, equipment availability and performance rates together. In addition to this preventative approach, it can empower operators to consider equipment performance and availability. Proactive action and optimization make sure everything is always running to its fullest potential.
![]()
Production tracking and genealogy
Tracking and genealogy are essential to any and every operation tackling the growing demand and needs of the world.
A MES offers a complete tracking of the production lifecycle. Genealogy allows to see how your products evolve while simplifying quality control to ensure you meet your industry standards. Traceability simplifies keeping track of where and when a product is in its lifecycle. In the event of a recall, you’re empowered to effortlessly provide all the necessary information to know what and where something might have gone wrong.

Quality management
As mass production becomes increasingly competitive, quality management is a growing concern.
With an increasing demand for intricate products to be produced and shipped a mile a minute, in-depth process tracking allows you to secure customer satisfaction. By automating aspects of quality assurance, your Quality Management is empowered with tracking and synthesizing manufacturing processes onto user-friendly dashboards. You can mitigate risks by documenting and centralizing the production without the worry of missing something important. You can also reduce risks thanks to preprogramed alarms and notifications.

Resources allocation and status
Increasing production often means an addition of newfound resource and planning challenges. A MES serves as a tower of strength to curb the greater number of worries catering to increasing demand.
By effectively connecting to and exchanging information in real time with administrative systems like an Enterprise Resource Planning software (ERP), resource management is made easy with an MES. This interconnectivity can then enable both executives and operators to oversee operations in terms of supply and demand.

Labor management
While an MES cannot yet autonomously manage factory floors and algorithmically organize as a quasi-symbiotic operation, it does greatly improve your planning capabilities.
Where labour management can often be tedious and downright daunting, the MES serves as a right hand for scheduling. Beyond Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) resource allocation, an MES-connected operation enables you to optimize shift planning based on work patterns, employee attribution and business needs. As time progresses and you learn about these strengths and weaknesses, you're empowered to support your teams exactly how they need.

Operations management and scheduling
By interconnecting your factory floor, you build a real-time summary to overview your processes.
An MES offers you a transparency that enables you to successfully plan for the best sequencing, as well as react when things go out of sync. By utilizing the interconnectivity between the MES and ERP, executives and operators can devise plans and scenarios according to your operational constraints. This planning effectively reduces losses, minimizes change-over time, and empowers your team to meet deadlines.

Production units dispatching
The MES’s manufacturing oversight grants you an increased agility in managing rapid change.
A MES grants you a better way to calculate for unforeseen dispatching adjustment requirements. This enabled reactivity ensures you proactively adjust to measurements, sizes, and time-sensitive processing. By helping you prevent these losses, the MES lets you maximize the flow of production based on your operational reality. For example, it can help differentiate fast-runners and slow-runners in palletizing to adjust for a quicker turnover.

Process management
The MES serves as a central hub in overseeing all the aspects of what goes on throughout the factory floor.
The MES grants a transparent view that helps set smart goals for your team. By utilizing ecosystem connectivity (such as ERP) and making sure that workorders are on track, executives can effectively aim to hit target production goals. Digitally recording procedures generates key metrics on production values to facilitate decision-making and best usage at all times.

Maintenance management
Whether you are working within the intricacies of watchmaking, or the mass-producing and bagging of food, periodic and preventative maintenance are crucial to ensure successful process completion.
By ensuring that servicing and checkups are done in a timely and perpetual manner, you significantly reduce the chances of mishaps. An MES effectively connects and gathers data on every aspect of productivity. This lets you know when repairs need to be done, preventing possible workplace injuries, and stops expensive repairs before they get worse.

Document management
Going paperless is one of the key features that attract a large number of inquiries to MES integration.
Implementing an MES offers to free its users from the tedious tasks related to paper-reliant practices. The paperless transition grants several advantages, such as automating the registry of inventory, or the digitalization of crucial production documents (like assembly plans). A MES grants more than data reassurance, by freeing up team members from recording and writing, you enable and empower them to do what they do best.
Position of the MES in an enterprise IT architecture
The ISA-95 pyramid is often cited as a visual representation of the smart manufacturing ecosystem. While the MES is shown to have an equidistant spot with the other aspects, it is undoubtedly more impressive. The MES will effectively connect the lower half to the business planning and logistics.
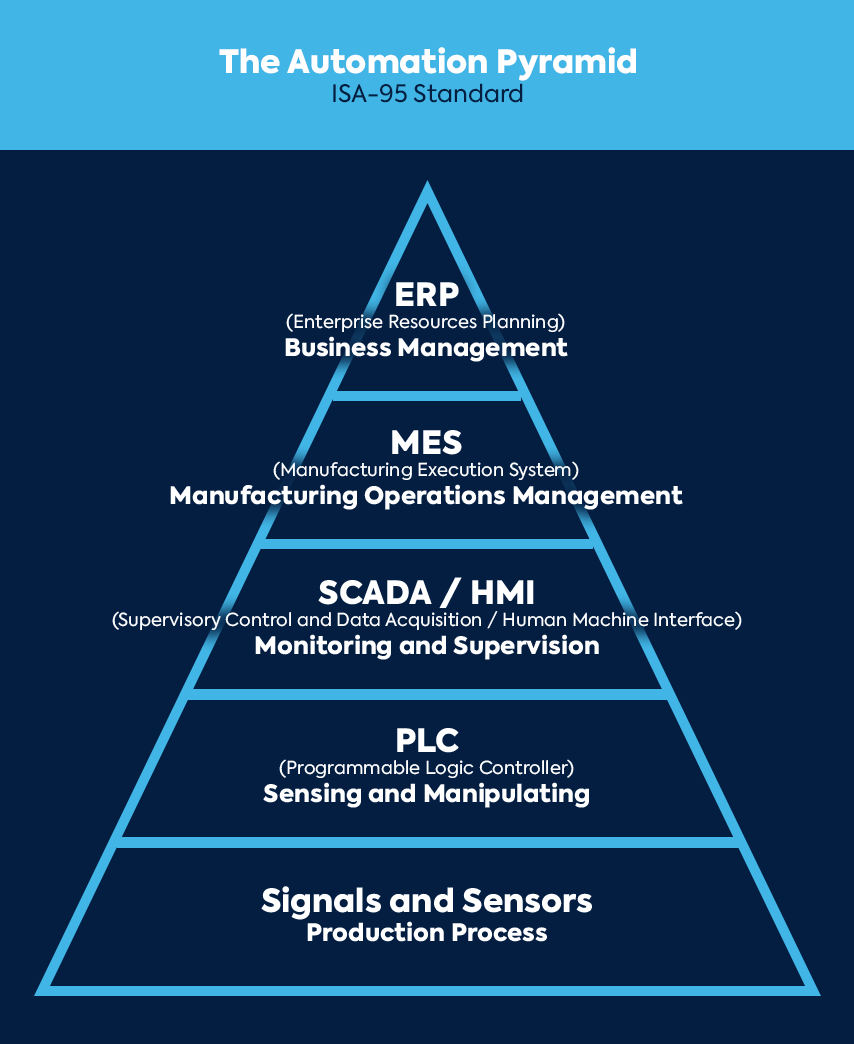
The Programmable Logic Controller (PLC ) will acquire data through the sensors and signals, which will be synthesized and forwarded to the Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Human Machine Interface (HMI) - these direct-contact interfaces can grant operator control of a machine. The control data is extended to the MES, where it is the most crucial in controlling an operation. The MES will communicate upwards and downwards between the ERP and the rest of the pyramid to control and optimize the production process.
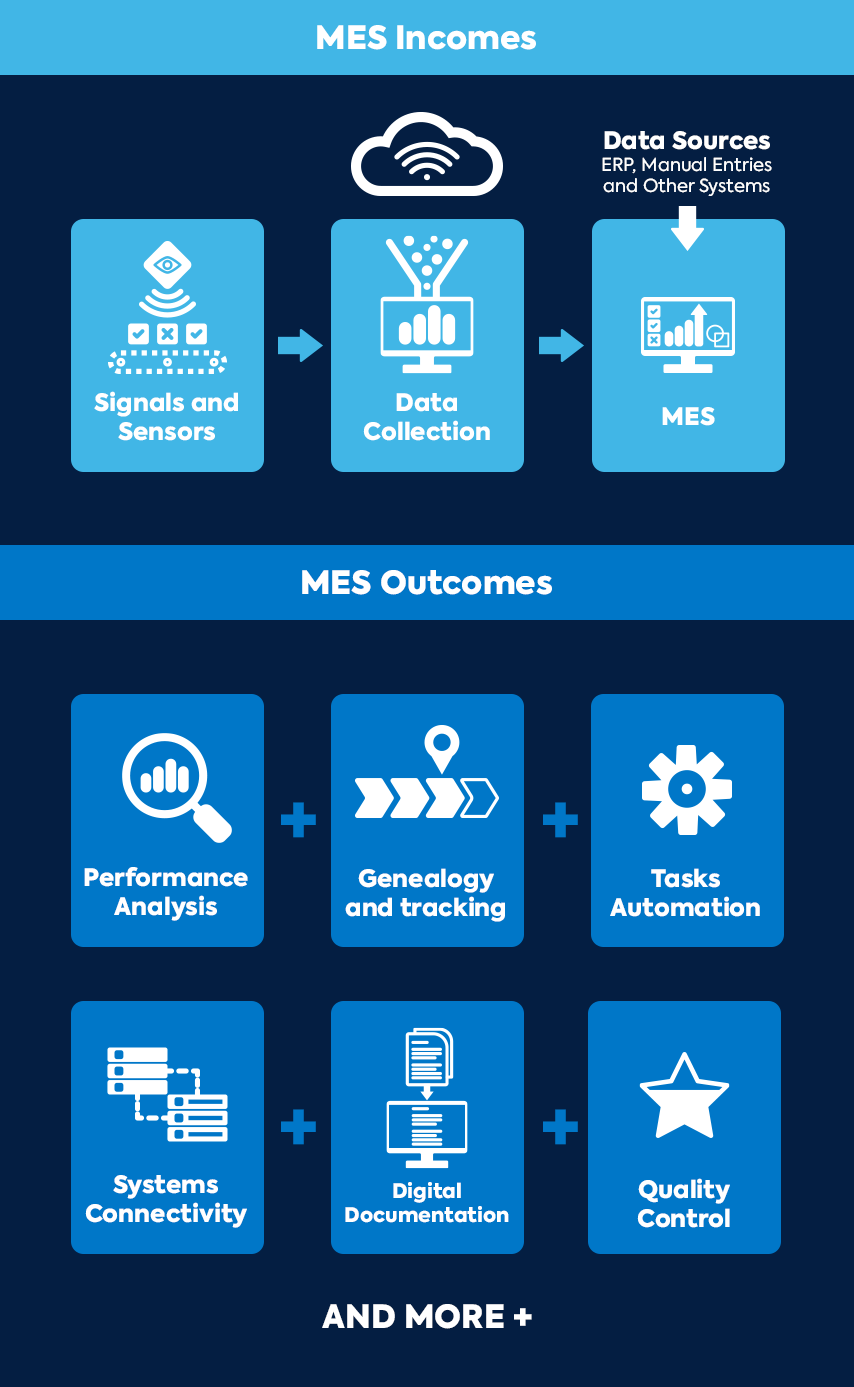
Essentially, the PLC will pick up a signal, like a temperature gauge, and communicate it to the SCADA (where the HMI can serve as a direct intervention in case of emergency) then through to the MES. The MES is really the step where the context of temperature is assigned and programmed to notify if it’s out of expected measurements. In a way, this data transfer it like sending an instant message between devices – it’s the background processes and software that do the work. The only difference is that it’s automated and continuous.
The enabled interconnectivity is the investment enabler. Collecting and visualizing data on the entire manufacturing operation lets you act based on reliable metrics to make decisions. Issues arise, no matter the operation. The MES grants you the capability to know why the downtime happened, what was affected, where it is now, and who can be assigned to solve the problem.
In terms of networks, the MES acts within the operational network. However, a rising number of MES solutions offer a hybrid or cloud-based set of functionalities and data storage which need connection to the internet and to the office network. In all cases, for a better use and a proper interconnectivity between an MES and all other systems, you'll have to grant a secured access through firewalls to ensure a fluid communication between your operational and administrative systems.
What are the limits of an MES?
In terms of customization, the MES can often wear your brand, be shaped to your operational realities, get connected to your other systems, and so on. However, there are limitations to keep in mind. Often, extensive and difficult customization accompanies a higher overall cost. This is due to the nature of the requests extending beyond what the software’s capabilities. Over-customized solutions can also inevitably limit your flexibility to alter aspects of the program autonomously.
As for applicative limitations, the MES resides in the barriers of which its counterparts act. It cannot solely gather and synthesize data. Its interconnectivity is what enables you to take decisive action and take control of your business.
There are also stark differences between digital solutions. For example, the MES will differ from the ERP, where the ERP willbe locked into simply providing managers with a general overview of manufacturing operation. The MES enables you to have a greater oversight, while also enabling your teams to hierarchically take advantage of the data.
How does an MES work?
A MES serves many functionalities to reach operational excellence.
PLC, HMI, and SCADA grant data flow from the equipment, but it is the MES that receives and organizes this data into understandable metrics. By utilizing this data, users are empowered with a complete synthesis based on their preferred visualization (graphs, trend views or dashboards) and can take actions to reach objectives.
Fundamentally, the MES will serve as an operation hub to ensure both complete control and benchmark performance to reach goals every time. The benefits reaped from this transparency extend to sequence optimization, maximization of turnover rates and output, loss prevention, simplified management, and much more.
How does MES collect manufacturing data?
Typically, a worker would have been responsible for collecting data from production by going to the physical machine and taking note of the points of interest. The MES simplifies this collection process by extracting and historicizing real-time manufacturing data from the interconnected PLCs.
As this data comes out in a raw and continuous flow, it needs to be contextualized to grasp what it is saying. The MES program will then be set to receive the data and will typically organize it by equipment and type and offer a user-friendly visualization. The MES also reassures safety by associating users to equipment to have a clear understanding of the who, what, where and when as part of its digitalization of data.
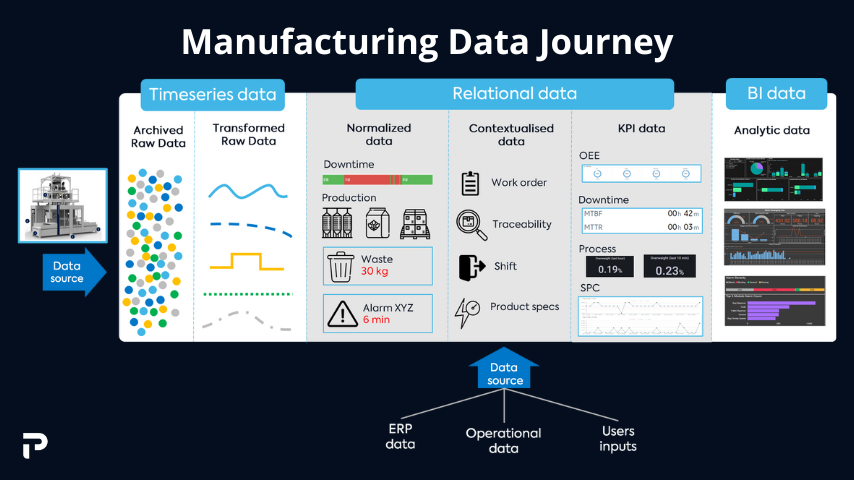
How to analyze manufacturing data?
The visualization of data will be effective in giving perspective to what is happening throughout the factory floor. Points of interest such as downtime, production completion, output, and waste tracking can be visualized through graphs and timelines to grant you a clear perspective to set and achieve goals. It also registers key metrics, such as temperatures, stock, servicing, and much more to give you an edge on maintenance and safety.
Through performance analysis and quality management, the MES ease the analytics of manufacturing by correlating various data to each other to measure key metrics such as OEE. Some MES solutions offer embedded BI and dashboarding tools to ease the visualization of data and compare equipment performance through the time.
Understanding manufacturing data is not always straightforward. It's important to have specialists in the operational team able to work with data. BI experts, process engineers, data scientists, and other data-driven team members can take up the title of MES champion. This champion will both be in charge of data analysis and will empower users to navigate and work with the data.
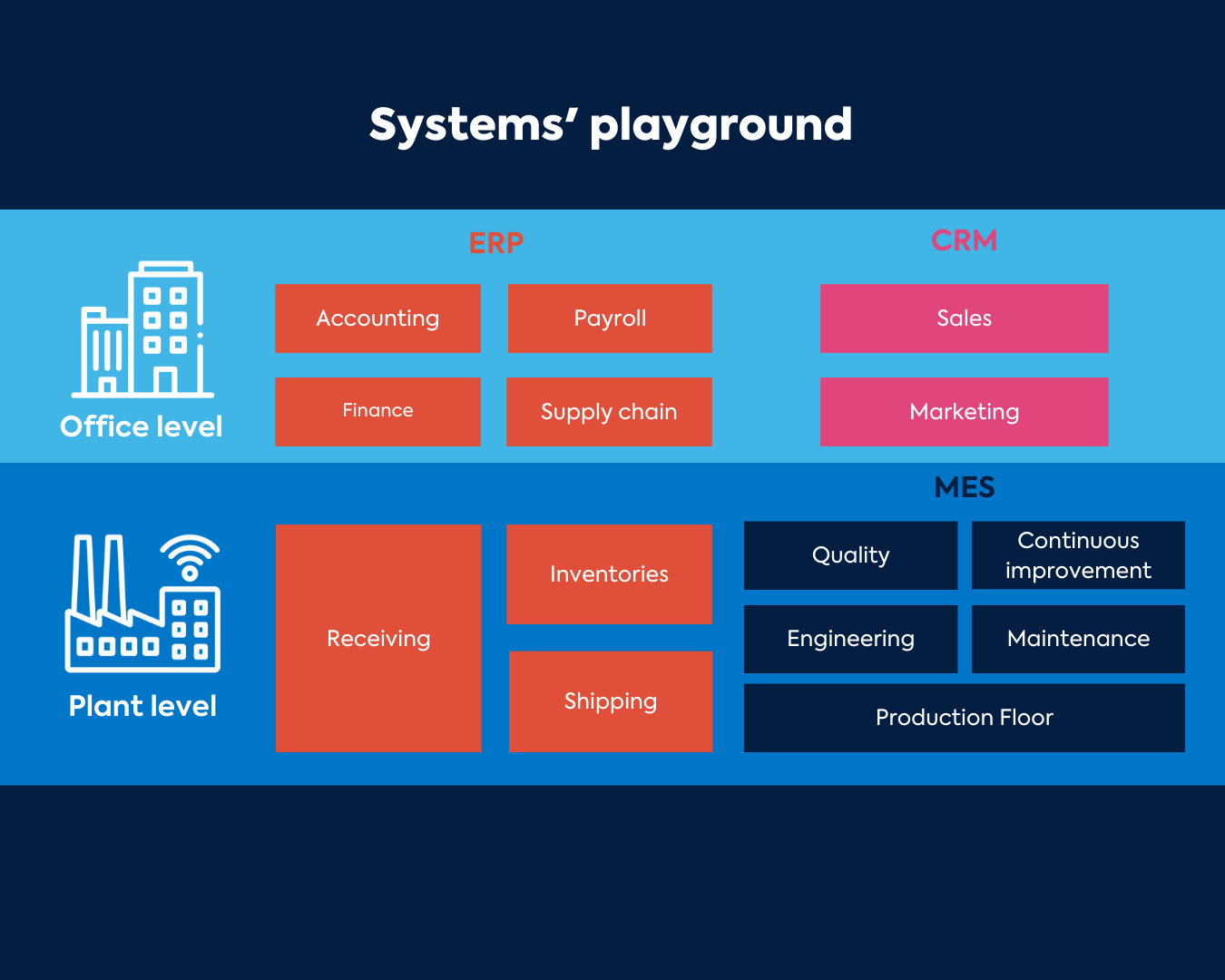
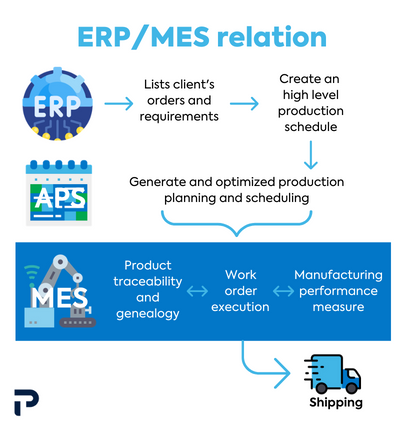
How does MES work with ERP?
The MES works on a Manufacturing Process level. Its goal is to maximize efficiency within the roles engineers, operators, plant managers and other employees have on the actual factory floor. Contrastively, the ERP works on the Enterprise Processes level. It manages order fulfilment, finances, forecasting; basically, the bigger picture.
The complementary relationship between the MES and the ERP is what enables manufacturers to excel. The MES serves as the point of contact between the ERP and the rest of the digital ecosystem within factory walls. An ERP will manage the macro aspects of the operation and feed the MES information on workorders for example. On the other hand, the MES will manage micro aspects and forward information on stock versus production rates to the ERP.
In a nutshell, both systems act as one unit to overview, manage, and proactively adjust a manufacturing plant operation.

Operations
Operational planning is made simple as the MES centralizes everything you need to know about how your assets are performing.
- Simplifying data collection: By interconnecting your manufacturing operation, you free up your operators from time-consuming data collection and opt for real-time access.
- Overall Equipment Efficiency: Become empowered to understand what can be improved in terms of your standard practices. Equipment turnover rates, sequencing, and resource management can be optimized to ensure the highest efficiency.
- Ensuring resource supply: Track and allocate your raw-material usage and make sure you never run out of supply.
- Operator management and scheduling: Manage users and optimize the scheduling of operators to ensure every station meets your goals.
- Preemptive machine maintenance: Visualization and metrics stop accidents before they happen, always ensure to take action on machine maintenance.

Quality
The MES ensures that keeping track of quality is simple and effective in order to maximize your outflow of production and curb extra costs.
- Track metrics: Ensure quality in every batch every time and guarantee quality by confirming production averages.
- Reduce losses: Tracking a constant stream of production data grants you a 6th sense to stop production as soon as issues arise and minimize loss.
- Product genealogy: Simplify the chance of recalls by automatically documenting the full production lifecycle of each item at all times.
- Traceability: Facilitate environmental and governmental compliance with a faster way to track products through their production cycle.

Senior management/Executive
The MES lets you excel in big picture planning and direction while pairing functionalities with your existing ERP software in terms of managing your assets and empowering your team.
- Workorders: Follow the flow of production and see what is being done and where, at all times.
- Tracking production cycle: Make sure every step of production is done flawlessly and follows your plan.
- Client relations: The MES allows you to simplify a deeper operational understating to inform clients and partners on timelines, and to have their insight on proactive adjustment.
- Centralized operation hub: Gain transparency, velocity, and accessibility by centralizing all of your points of interest.

Finance
Financial planning is made simple with a constant flow of information that ensure everything that needs to be addressed is addressed without waiting for the aftermath of costly mishaps.
- Enhancing Profitability: Granting you operational teams with tools to manage their staff allow them to manage both equipment and resources more efficiently, effectively producing with smaller margins.
- Optimizing Storage and Supply: Never run out of raw materials. Plan in advance with tighter resource and production management and ordering your resources when they’re needed.
- Asset management: proactively plan out your assets to maximize the return while mitigating risks like proactive maintenance.

Additional Points
- Innovation: Real-time accessible production data grants you significant insight that will fuel your innovation process.
- Rejuvenate Sales: Work to support sales with transparent information access and optimize production planning to meet deadlines and offer unfaltering quality.
Types of MES
While the needs for smart manufacturing solutions are ever growing, there is no ‘one-size fit all’ solution. Instead, a MES can be sought out to meet your industry-specific needs, such as a having predisposed functionalities to accommodate for agricultural processing lines, appliance and technology lines, automobile and heavy machinery lines, and more.
MESs can have major differences in terms of storage and accessibility. Different types of approaches can be utilized to meet your operational reality.
Cloud, On-Premises, and Hybrid Solutions
On-premise systems are solutions that can store all of your data on-site physically. These types of accommodations will typically be sought out by industries dealing with extremely sensitive information or those who do not need to extend any information whatsoever out of their site. On-premise systems do require a great deal of investment in terms of storage capacity and maintenance beyond the purchase of hardware and servers.
On the other hand, Cloud-based systems are the opposite of on-premises systems. They are very effective in splicing and organizing data to maximize the use of storage. Cloud solutions offer an easier scalability, as you do not need to purchase aditional heavy hardware t scale your systems; this further results in lower initial investments, as the cost approach turns to low subscription fees. Cloud-based solutions offer additional advantages in terms of mixed-mode manufacturing and multi-site configuration: since you don't require physical implementations across plants, clud systems can be jumpstarted with less on-site resources and assets.
Cloud-based MES
Advantages
- Scalable and faster configuration
- Lower initial investment
- Multiple-platform accessibility
- Supports mix-mode manufacturing
- Standard multi-site configuration
- Automatic security firmware updating and backup
Points to consider
- Requires a dedicated cloud-IT
- Internet-reliant system
- Recurrent Cloud subscription fees
Cloud-based MES
Advantages
- Scalable and faster configuration
- Lower initial investment
- Multiple-platform accessibility
- Supports mix-mode manufacturing
- Standard multi-site configuration
- Automatic security firmware updating and backup
Points to consider
- Requires a dedicated cloud-IT
- Internet-reliant system
- Recurrent Cloud subscription fees
On-premise MES
Advantages
- On-site secure data access
- Able to manage heavier loads of raw data
- Greater customization of solution
- Full control of privacy and security
- Software ownership
Points to consider
- Costly scalability and maintenance
- Separate setups for different plants
- Dedicated hardware-IT
On-premise MES
Advantages
- On-site secure data access
- Able to manage heavier loads of raw data
- Greater customization of solution
- Full control of privacy and security
- Software ownership
Points to consider
- Costly scalability and maintenance
- Separate setups for different plants
- Dedicated hardware-IT
A hybrid MES solution combines the advantages of both cloud-based and on-premises solutions, providing the flexibility and scalability of the former and the security and control of the latter. It allows businesses to customize their MES solution, choosing which components to keep on-premises and which to move to the cloud. A hybrid solution can provide greater uptime and business continuity by combining the redundancy and failover capabilities of both on-premises and cloud-based systems. Overall, a hybrid MES solution offers a versatile solution that meets the needs of modern manufacturing businesses. There are still some considerations to keep in mind with hybrid solutions, such as hardware management or a partial reliance to the internet.
Production Monitoring System vs MES
While a Production Monitoring System (PMS) may offer similar advantages to an MES, it does not offer the same breadth and depth of analysis. A PMS may be advantageous to small enterprises with limited budgets; however, the MES suite will be the driver of automation in terms of business scalability and production.
PMS
Advantages
- Inexpensive and easy setup
- Suits smaller business needs
- Quick basic view of your equipment/processes
Points to consider
- Limited and industry-specific functionalites
- Difficult to scale (non-evolutive)
- Limited data collection
PMS
Advantages
- Inexpensive and easy setup
- Suits smaller business needs
- Quick basic view of your equipment/processes
Points to consider
- Limited and industry-specific functionalites
- Difficult to scale (non-evolutive)
- Limited data collection
MES
Advantages
- Greater depth and breadth of functionalities
- Easier to scale the solution
- Greater data quality and advanced analysis
- Offers short and long-term advantages
Points to consider
- Significant initial investment
- Longer implementation time
MES
Advantages
- Greater depth and breadth of functionalities
- Easier to scale the solution
- Greater data quality and advanced analysis
- Offers short and long-term advantages
Points to consider
- Significant initial investment
- Longer implementation time
Industry Specific vs Generic MES solutions
There is specific use-case software that will be tailored to accommodate for different types of industry, as well as more generic MES.
For example, GE Digital Plant App and SAP MII will typically offer a flexible generic system; however, this can result in additional implementation costs to ensure a minimum level of customization. The industry-specific MES will be designed to highlight known points-of-interest, such as tailored KPI, tracking, and other functionalities required per industry.
Industry-specific MES
Advantages
- Rapid implementation
- Industry-specific KPIs and tracking
- Complies with the industry’s standards
Points to consider
- Less flexible and agile
- Limited single focus process tracking
- Difficult to scale (non-evolutive)
Industry-specific MES
Advantages
- Rapid implementation
- Industry-specific KPIs and tracking
- Complies with the industry’s standards
Points to consider
- Less flexible and agile
- Limited single focus process tracking
- Difficult to scale (non-evolutive)
Generic MES
Advantages
- Greater Flexibility
- Supports different types of manufacturing
- Supports a greater range of functionalities
Points to consider
- Higher implementation costs
- Additional configuration
Generic MES
Advantages
- Greater Flexibility
- Supports different types of manufacturing
- Supports a greater range of functionalities
Points to consider
- Higher implementation costs
- Additional configuration
How to choose the right MES for your business?
This section aims to equip you with the right toolset and criteria to finding the right solution for your needs. The desire for automation means you need to think about a large number of things; for example, what type of infrastructure you have in place, what type of signals you’re trying to gather, can your methods get up to speed and utilize advanced technology, among others.
Criteria to consider when selecting an MES

IT Infrastructure
Consider what can your current IT infrastructure support. Assuming you have potential to interconnect, you’ll need to find out your data and security needs in order to know what kind of traffic the system will need to support.

Current automation level
Looking at your current manufacturing equipment, are your PLCs up to date? Can your machines be connected? By looking if your operation meets the prerequisites, you can set a plan to either go ahead or revisit what needs to be brought up-to-speed.

Equipment to connect and available signals
Layout a plan as to identify what equipment and which processes you want to connect to gather data on. While it may seem tempting to go ahead and want to get the full kit, depending on your situation it may be advantageous to start small and scale with due time.

MES Project ownership
In terms of project management, enterprises will typically aim to have a power user, or champion to act as a catalyst to introduce, and eventually train operators to utilize the digital tools. It is then crucial to choose a dedicated champion to spearhead the implementation with the integrator.

Manufacturing Data Strategy
To lead to a successful implementation, there is a crucial need to distinguish what the desired outcomes are. A lot of data can be extracted from interconnect operations; However, not all of this data needs to be visualized if it does not serve an inherent purpose. A good data strategy is important as it can effectively curb costs and speed up integration.

Digital Transformation Vision
Long-term planning is highly recommended as integration typically sees a gradual expansion and desire for accommodating a greater number of facets within production. It is important to dedicate time to getting to know your end goals, where you need your data to go, and what can eventually be optimized. There is no doubt that the MES will serve as a foundational pillar in your digital transition. A plan is necessary to achieve your greatest potential.
A MES project will offer an outcome as successful as its planning. Therefore, it is crucial to know what you’re getting into. In short, you need to ensure that you plan out your exact needs, lay out your priorities, and map out the implementation process with your integrator.
How much does an MES cost?
There is no clear-cut way to define the exact cost down to the dime, however we can generate an estimate. Like any good solution, you must look at it in steps. It’s no surprise that Manufacturing Execution Systems come in a well-defined and organized tally. Additionally, there a several advantageous outcomes to consider.
While an MES has an attractive price point compared to other enterprise solutions, there are fees to consider in terms of the entirety of the project.
- Licensing fee: this fee is what you’ll pay to have access to the software. Licenses give you access to modules and features that come with your plan. Usually, the software will come ready-to-use for a generic installation but can require personalization. This fee is charged on an annual basis.
- Personalization fees aren’t clear-cut; however, they are usually calculated on the time spent configuring your desired customization to the software and what has been discussed with the integrator. These are normally one-time fees but can result in long-term costs.
- Integration fees are those that a certified integrator will charge to work with you to set up the system. These can come in the form of a bundle package, an hourly rate, or a mix of both.
- Hardware fees will depend on the solution you may opt for. On-site cloud solutions with an edge computer and on-premise solutions can vary costs in terms of hardware, installations, and long-term costs.
- Training fees will vary (or be included) depending on the integrator. Training is typically provided through a power user, or a set of power users, before moving onto the greater half of the operation.
- Maintenance fees will become a regular annual occurrence to keep your systems in tip-top shape as the solution becomes a staple in your operation.
- Support fees come with any professional services provider. Your integrator will often offer a support contract to help clients with troubleshooting, software updating and other actions that will keep the MES efficient and powerful. Software editor can also offer this kind of support contract. These fees will typically be in the form of a bundle package, an hourly rate, or a mix of both.
- Ancillary costs may also be brought up as the MES integration touches many departments within your enterprise (IT, quality, operator, maintenance, HR, etc.) Therefore, should be planned for in the form of investing in yourself.
Once integrated, the Manufacturing Execution System's advantages rapidly become apparent. By optimizing and therefore maximizing your production, you ensure a reliable production sequence and greater profit margin.
How to calculate the ROI of an MES?
Along with the advantages of optimizing your manufacturing procesess, the MES is often initially calculated in terms of savings. These savings and advantageous outcomes range as follows:
- Minimizing Labour is a well-known advantage of MES integration. Interconnectivity and tracking all processes translate to being able to allocate resources where they need to be without worry. This means you get significant savings in terms of preventing overstaffing.
- Loss Prevention is made simple by having a constant flow of information. You can effectively ensure all of the aspects of production meet requirements to maximise the outflow. As any business knows, a reduction in loss translates to a significant financial advantage.
- Resource Allocation Optimization means you can effectively do more with less. By integrating an MES, and consequently being able to keep a diligent tracking of resources, you can make sure you never overstock or run out of raw material. This means you can simplify budget allocation and ensure a seamless production.
Implementation and deployment of MES
Whether you’re looking into a generic or industry-specific solution, it’s no surprise that no MES comes in as a plug and play. Typically, a dedicated integration team will take the lead of the project based on your specific needs. The decision on whether it is more advantageous to opt for a generic or industry-specific solution will be determined during your preliminary discussions.
At a glance, the first step to integration is ensuring the infrastructure is connectable via PLCs and HMIs. From there, initial data can be gathered for specialists to organize and contextualize them to grant autonomous reporting. The MES quickly takes over the data contextualization and the integrator efforts are focussed on ensuring you have a transparent view of your operation with graphs and digital tools.
Once the system is set up, you can plan for team integration and a preliminary procedure update. Once data is gathered to calculate KPIs and OEE, you can then proactively adjust to ensure maximum production and profitability.
How to learn MES?
There’s not a unique and simple way to learn to use, or master, an integrated Manufacturing Execution System. You must first identify your needs, and then get the help of specialists to properly integrate a solution.
Typically, digital transformation is spearheaded by a champion, or power user working with the integration team. This champion is brought up to speed on the functionalities and is the catalyst between the executives and eventually trains the operators. More often than not, many integrators will cut ties with industries when they seem self-reliant. However, this can be problematic when challenges arise.
The best integrators will offer a comprehensive continuous support and form long-term partnerships to assist you in the entirety of your digitalization. Integration is truly a first step in this digital evolution, assisting you in dealing with change, with unpredictable situations, cyber security and much more, you can discover what a true digital partner can do through our services.
Related Articles

Join the Future of Manufacturing
Don’t get left behind in the rapidly evolving manufacturing industry 4.0. Partner with Premier Tech Digital and unlock the potential of Industry 4.0 with our solutions and expertise. Experience the future of manufacturing today!








